Blockchain technology is flipping how we think about data, transactions & trust. You’ve probably heard of it, especially with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. But hang on, there’s a whole lot more to blockchain than just digital money.
Table of Contents
ToggleThere are various types of blockchain technologies, each fit for different purposes. Knowing these types can help you better understand what blockchain can do. In this post, we’ll break down the four main types: public, private, consortium, and hybrid.
Let’s get into it.
What Is Blockchain Technology?
Before going into the types, let’s quickly talk about what blockchain technology is. In simple terms, blockchain is a way to store data that’s secure and decentralized. Each piece of data lives in a block, and these blocks link together to form a chain. That’s why it’s called a “blockchain.”
The big idea here? No single person controls the whole chain. Instead, data spreads across many places, making it tough to mess with. This builds trust without needing a central authority.
Now that you know the basics, let’s look at the four different types of blockchain.
Also Read – What is Blockchain? Everything You Need to Know
1- Public Blockchain
What Is a Public Blockchain?
A public blockchain lets anyone join in. Yep, it’s decentralized — meaning no one governs it all alone. Anyone with internet can join in, check the data & even validate transactions or add new blocks.
Bitcoin and Ethereum are popular public blockchains. These platforms let users transfer digital money, make decentralized apps (dApps), and create smart contracts.
How Does It Work?
In public blockchains, users depend on a consensus mechanism to verify and add transactions. The common methods? Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS).
Proof of Work (PoW): Miners race to solve tricky math puzzles. The first one to solve gets to add the next block & earn a prize.
Proof of Stake (PoS): Instead of competing with power, users “stake” their coins for a chance to add a block. More coins staked mean higher chances.
Public blockchains are super secure ’cause many users & nodes maintain them. But this also makes them slower and energy-hungry.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Open to everyone
- Decentralized & transparent
- High security
Cons:
- Slow transaction times
- High energy use (especially PoW networks)
2- Private Blockchain
What Is a Private Blockchain?
As the name says, private blockchains are closed networks. Only authorized folks can access them — great for businesses and organizations needing control over who sees their data.
In private blockchains, the owner decides who can participate or make changes. They’re often used for internal processes or supply chain management.
How Does It Work?
Private blockchains usually use Proof of Authority (PoA). In PoA, instead of loads of people validating transactions, select trusted nodes (validators) have the power to approve new blocks. This makes private blockchains fast at processing transactions compared to public ones.
Because only chosen folks can join in, private blockchains are more centralized. This lowers outside tampering risks but means trusting those running it.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Fast & efficient
- Controlled access useful for businesses
- Low energy use
Cons:
- Centralized—less transparency
- Relies on trusted authority figures
3- Consortium Blockchain
What Is a Consortium Blockchain?
A consortium blockchain is somewhat of a middle ground between public and private blockchains. It is a semi-decentralized system where multiple organizations manage the blockchain together. This type of blockchain is also known as a federated blockchain.
For example, a group of banks might use a consortium blockchain to handle inter-bank transactions. This allows for greater collaboration while still maintaining some control over who can access the network.
How Does It Work?
In this system, various entities (companies, let’s say) run the nodes that validate transactions. These guys team up to agree on the network stuff. Because only trusted folks are involved, it’s way faster than public blockchains.
These blockchains use different consensus systems, and one favourite is Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT). BFT makes sure everything works right even if some nodes mess up.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Let multiple organisations work together.
- Quick and efficient.
- Safer than fully centralized setups.
Cons:
- Trust is still needed among participants.
- Not as transparent as public blockchains.
3- Hybrid Blockchain
What Is a Hybrid Blockchain?
A hybrid blockchain is like having the best of both worlds. It mixes public and private elements, giving you the choice to keep some info public while hiding other stuff. Perfect for groups needing both transparency and secrecy.
For instance, in healthcare, patient data stays private, but research results can be shared with everyone.
How Does It Work?
With a hybrid blockchain, the boss decides what stays public and what’s kept secret. Transactions get verified in public or in private – depending on the rules of the network. This gives loads of flexibility; secret stuff stays hidden while other actions can go public.
The setup can also let people interact with some parts of the blockchain without full access. Like, they might verify transactions but won’t see confidential bits.
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Balances openness with privacy.
- Adaptable to needs.
- More control over who sees what.
Cons:
- Tough to set up and manage.
- Still needs trust in entities handling the private side.
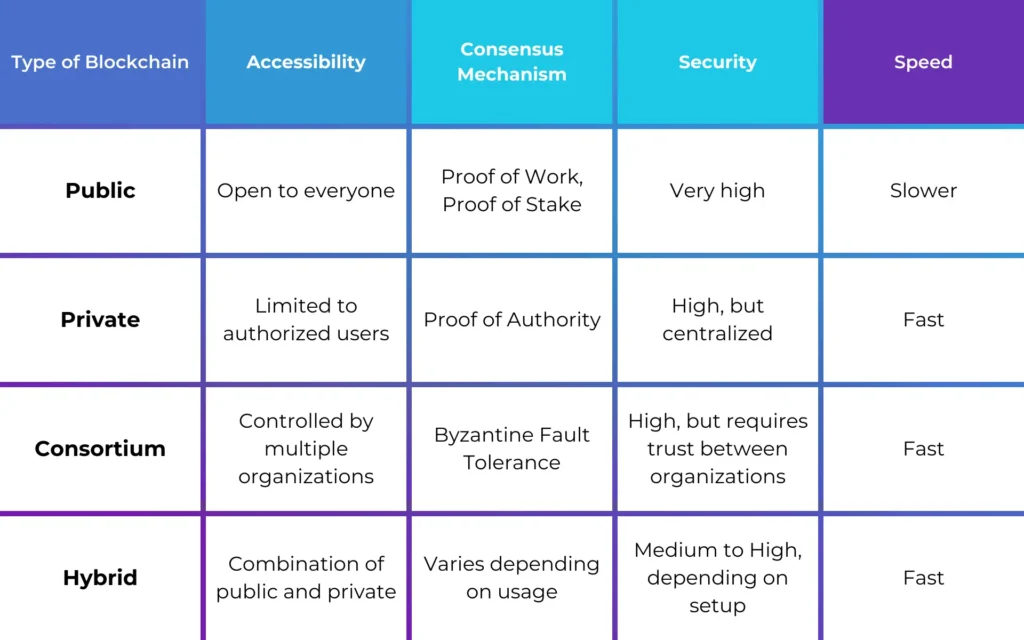
Key Differences Between Blockchain Types
Let’s summarize the differences between these blockchain types to make things clear.
Conclusion
Alright, let’s wrap things up. Blockchain is super cool, but it’s not a one-size-fits-all kinda deal. You’ve got your public, private, consortium, and hybrid blockchains, each bringing something special to the table. Public ones? They give you transparency & decentralization but sacrifice speed and gobble lots of energy. Private blockchains are quick and under control but put all your trust in the authority running ’em. Consortium blockchains? These let multiple organizations work together, which is pretty neat. And then there are hybrid blockchains—these balance privacy with transparency, making them fit just right for specific needs.
Knowing these different kinds of blockchains is important. As blockchain keeps growing and changing, we’ll see new ways it can be used—and that’s super exciting! Whether you’re a tech geek or just starting to figure this stuff out, getting the hang of these basics will help you stay ahead of the game in the fast-paced world of blockchain.


